Resveratrol and Its Effects on the Vascular System
Johannes M. Breuss 1, Atanas G. Atanasov 2,3 and Pavel Uhrin 1,*
1 Department of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research, Center for Physiology and Pharmacology, Medical University of Vienna, 1090 Vienna, Austria; Johannes.Breuss@meduniwien.ac.at
2 Department of Molecular Biology, Institute of Genetics and Animal Breeding of the Polish Academy of Sciences, Jastrz˛
Received: 28 February 2019; Accepted: 23 March 2019; Published: 27 March 2019
Abstract
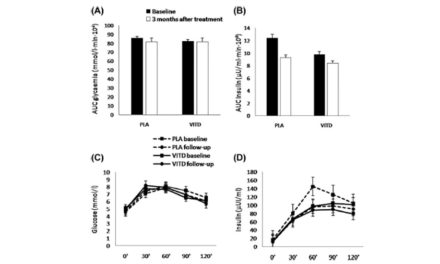
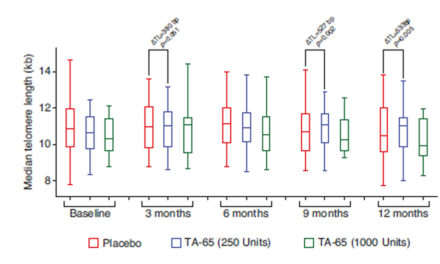
Resveratrol, the phenolic substance isolated initially from Veratrum grandiflorum and richly present in grapes, wine, peanuts, soy, and berries, has been attracting attention of scientists and medical doctors for many decades. Herein, we review its effects on the vascular system. Studies utilizing cell cultures and pre-clinical models showed that resveratrol alleviates oxidative stress and inflammation. Furthermore, resveratrol suppresses vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, promotes autophagy, and has been investigated in the context of vascular senescence. Pre-clinical models unambiguously demonstrated numerous vasculoprotective effects of resveratrol. In clinical trials, resveratrol moderately diminished systolic blood pressure in hypertensive patients, as well as blood glucose in patients with diabetes mellitus. Yet, open questions remain, as exemplified by a recent report which states that the intake of resveratrol might blunt certain positive effects of exercise in older persons, and further research addressing the framework for long-term use of resveratrol as a food supplement, will stay in demand.
Keywords
resveratrol; clinical studies; cardiovascular disease; vasculoprotective effects