Triterpenoids and polysaccharide peptides-enriched Ganoderma lucidum: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study of its antioxidation and hepatoprotective efficacy in healthy volunteers
Hui-Fang Chiu a, Hui-Yu Fu b, Yan-Ying Lu c, Yi-Chun Han b, You-Cheng Shen d, Kamesh Venkatakrishnan b,Oksana Golovinskaia e and Chin-Kun Wang b
a Department of Chinese Medicine, Taichung Hospital, Ministry of Health and Well-being, Taichung, Taiwan, Republic of China; b School of Nutrition, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City, Taiwan, Republic of China; c Department of Neurology, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City, Taiwan, Republic of China; d School of Health Diet and Industry Management, Chung Shan Medical University, Taichung City,
Taiwan, Republic of China; e Department of Food Science, ITMO University, Saint-Peterburg, Russia
Abstract
Context—Ganoderma lucidum (Leyss: Fr) Karst. (Polyporaceae) is an oriental medicinal fungus, commonly used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for treating various condition or diseases such as hypertension,
hyperglycaemia, hepatitis and cancer.
Objective— The current study examines whether triterpenoids and polysaccharide-enriched G. lucidum (GL) influence antioxidation and hepatoprotective efficacy by suppressing oxidative stress.
Materials and methods— Forty-two healthy subjects (22 male and 20 female) were recruited and segregated into two groups as experimental or placebo and requested to intake GL (n¼21) or placebo (n¼21)
capsule (225mg; after lunch or dinner) for six consecutive months and vice versa with one month washout period in between. The anthropometric analysis and biochemical assays, as well as abdominal ultrasonic
examination were performed.
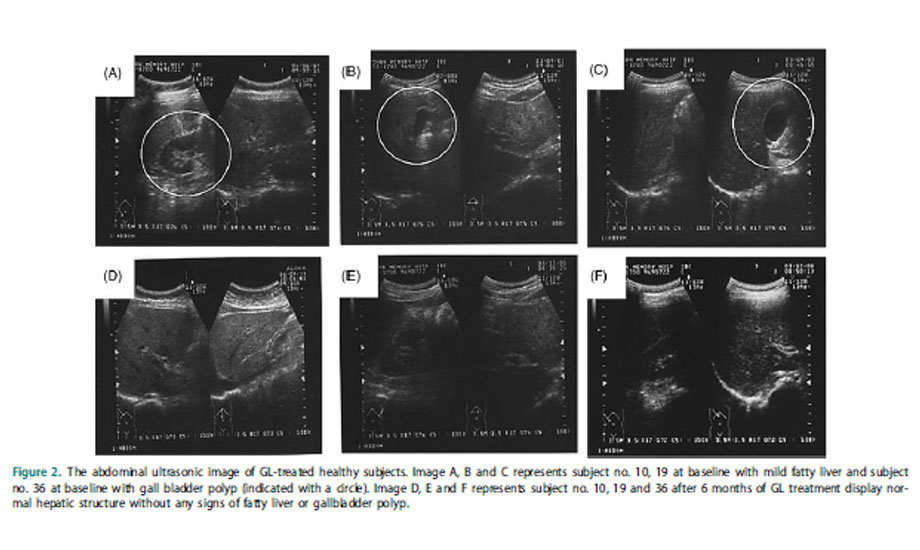
Results— Consumption of GL substantially improved (p<0.05) the total antioxidant capacity (TEAC; 79.33–84.04), total thiols and glutathione content (6–8.05) in plasma as well as significant (p<0.05) enhanced the activities of antioxidant enzymes. Whereas, the levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS; 3.37–2.47), 8-hydroxy-deoxy-guanosine (8-OH-dG; 15.99–11.98) and hepatic marker enzymes (glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase; GOT and glutamic-pyruvic transaminase; GPT) were concomitantly reduced (42 and 27%) on treatment with GL. Furthermore, the abdominal ultrasonic examination in GL subjects displayed a notable alteration on hepatic condition by reversing from mild fatty liver condition (initial) to normal condition.
Discussion and Conclusion— The outcome of the present intervention demonstrated the antioxidation,
anti-aging and hepatoprotective nature of GL by effectively curbing oxidative stress.
Keywords
Oxidative stress; ultrasonic examination; hepatic markers; fatty liver (…)